Subarea 1: Stem Cell Aging
The individual research groups within Subarea 1 investigate the causes and consequences of stem cell aging. The research work spans from basic model organisms over genetic mouse models up to humanized mouse models engrafted with human stem cells.
According to the FLI, with the closure of two groups since 2016 the representation of invertebrate models of stem cell research was reduced in Subarea 1. The institute presumes that the recruitment of new groups should fill this gap.
The research is defined by four focus areas:
- Cell-intrinsic mechanisms limiting the function of aging stem and progenitor cells,
- Aging-associated alterations of stem cell niches and the systemic environment,
- Mechanisms of clonal selection and epigenetic drifts in stem cell aging, and
- Microbiota- and metabolism-induced impairments in stem cell function during aging (in context of the new focus area Microbiota and Aging currently being built up within Subarea 2).
Research focus of Subarea 1.
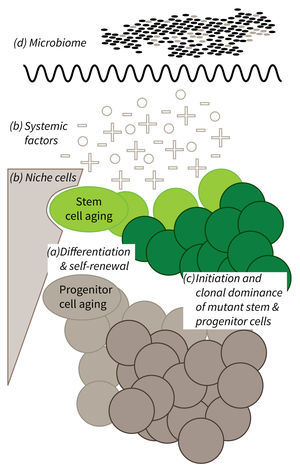
a) It is currently not well understood what mechanisms impair cellular functions in aging. b) The relative contribution of niche cells and systemic acting factors on stem cell aging have yet to be determined in different tissues. c) Clonal expansion of mutant cells associates with disease development in aging humans. Mechanistically, the process remains poorly understood. Changes in color intensity depict clonal dominance originating from stem (green) or progenitor cells (gray). d) Emerging evidences indicate that aging associated alter ations in microbiota influence stem cell function and vice versa.
Publications
(since 2016)
2020
- SIRT7: an influence factor in healthy aging and the development of age-dependent myeloid stem-cell disorders.
Kaiser A, Schmidt M, Huber O, Frietsch JJ, Scholl S, Heidel FH, Hochhaus A, Müller JP, Ernst T
Leukemia 2020, 34(8), 2206-16 - Cohesin controls intestinal stem cell identity by maintaining association of Escargot with target promoters.
Khaminets A, Ronnen-Oron T, Baldauf M, Meier E, Jasper H
Elife 2020, 9, e48160 - Publisher Correction: The mutational impact of culturing human pluripotent and adult stem cells.
Kuijk E, Jager M, van der Roest B, Locati MD, Van Hoeck A, Korzelius J, Janssen R, Besselink N, Boymans S, van Boxtel R, Cuppen E
Nat Commun 2020, 11(1), 3932 - Prevalence and dynamics of clonal hematopoiesis caused by leukemia-associated mutations in elderly individuals without hematologic disorders.
Midic D, Rinke J, Perner F, Müller V, Hinze A, Pester F, Landschulze J, Ernst J, Gruhn B, Matziolis G, Heidel FH, Hochhaus A, Ernst T
Leukemia 2020, 34(8), 2198-205 - Aneuploidy-inducing gene knockdowns overlap with cancer mutations and identify Orp3 as a B-cell lymphoma suppressor.
Njeru* SN, Kraus* J, Meena* JK, Lechel A, Katz SF, Kumar M, Knippschild U, Azoitei A, Wezel F, Bolenz C, Leithäuser F, Gollowitzer A, Omrani O, Hoischen C, Koeberle A, Kestler** HA, Günes** C, Rudolph** KL
Oncogene 2020, 39(7), 1445-65 * equal contribution, ** co-corresponding authors - SHP1 regulates a STAT6-ITGB3 axis in FLT3ITD-positive AML cells.
Reich D, Kresinsky A, Müller JP, Bauer R, Kallenbach J, Schnoeder TM, Heidel FH, Fässler R, Mann M, Böhmer FD, Jayavelu AK
Leukemia 2020, 34(5), 1444-9 - PLCγ1 suppression promotes the adaptation of KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinomas to hypoxia.
Saliakoura M, Rossi Sebastiano M, Pozzato C, Heidel FH, Schnöder TM, Savic Prince S, Bubendorf L, Pinton P, A Schmid R, Baumgartner J, Freigang S, Berezowska SA, Rimessi A, Konstantinidou G
Nat Cell Biol 2020, 22(11), 1382-95 - Elevated Hedgehog activity contributes to attenuated DNA damage responses in aged hematopoietic cells.
Scheffold A, Baig AH, Chen Z, von Löhneysen SE, Becker F, Morita Y, Avila AI, Groth M, Lechel A, Schmid F, Kraus JM, Kestler HA, Stilgenbauer S, Philipp M, Burkhalter MD
Leukemia 2020, 34(4), 1125-34 - Wnt7a Counteracts Cancer Cachexia.
Schmidt M, Poser C, von Maltzahn J
Mol Ther Oncolytics 2020, 16, 134-46 - Isolation and ex vivo cultivation of single myofibers from porcine muscle.
Stange K, Ahrens HE, von Maltzahn J, Röntgen M
In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 2020, 56(8), 585-92