Subarea 1: Stem Cell Aging
The individual research groups within Subarea 1 investigate the causes and consequences of stem cell aging. The research work spans from basic model organisms over genetic mouse models up to humanized mouse models engrafted with human stem cells.
According to the FLI, with the closure of two groups since 2016 the representation of invertebrate models of stem cell research was reduced in Subarea 1. The institute presumes that the recruitment of new groups should fill this gap.
The research is defined by four focus areas:
- Cell-intrinsic mechanisms limiting the function of aging stem and progenitor cells,
- Aging-associated alterations of stem cell niches and the systemic environment,
- Mechanisms of clonal selection and epigenetic drifts in stem cell aging, and
- Microbiota- and metabolism-induced impairments in stem cell function during aging (in context of the new focus area Microbiota and Aging currently being built up within Subarea 2).
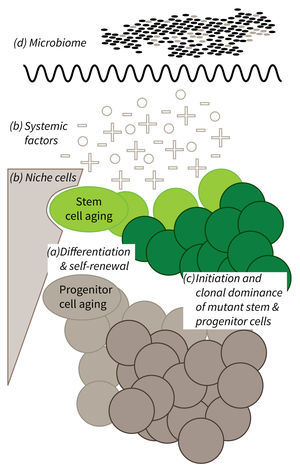
Research focus of Subarea 1.
a) It is currently not well understood what mechanisms impair cellular functions in aging. b) The relative contribution of niche cells and systemic acting factors on stem cell aging have yet to be determined in different tissues. c) Clonal expansion of mutant cells associates with disease development in aging humans. Mechanistically, the process remains poorly understood. Changes in color intensity depict clonal dominance originating from stem (green) or progenitor cells (gray). d) Emerging evidences indicate that aging associated alter ations in microbiota influence stem cell function and vice versa.
Publications
(since 2016)
2020
- Impaired metabolic stress responses in hematopoietic stem cell aging
Chen Y
Dissertation 2020, Jena, Germany - In utero lentiviral transduction of the gastrointestinal tract
Garside G
Dissertation 2020, Jena, Germany - Region-Specific Proteome Changes of the Intestinal Epithelium during Aging and Dietary Restriction.
Gebert N, Cheng CW, Kirkpatrick JM, Di Fraia D, Yun J, Schädel P, Pace S, Garside GB, Werz O, Rudolph KL, Jasper H, Yilmaz ÖH, Ori A
Cell Rep 2020, 31(4), 107565 - Fasting for stem cell rejuvenation.
González-Estévez C, Flores I
Aging (Albany NY) 2020, 12(5), 4048—4049 - DNA Methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) Function Is Implicated in the Age-Related Loss of Cortical Interneurons.
Hahn A, Pensold D, Bayer C, Tittelmeier J, González-Bermúdez L, Marx-Blümel L, Linde J, Groß J, Salinas-Riester G, Lingner T, von Maltzahn J, Spehr M, Pieler T, Urbach A, Zimmer-Bensch G
Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 639 - Skeletal muscle aging - stem cells in the spotlight.
Henze H, Juliane Jung M, Ahrens HE, Steiner S, von Maltzahn J
Mech Ageing Dev 2020, 189, 111283 - Splicing factor YBX1 mediates persistence of JAK2-mutated neoplasms.
Jayavelu AK, Schnöder TM, Perner F, Herzog C, Meiler A, Krishnamoorthy G, Huber N, Mohr J, Edelmann-Stephan B, Austin R, Brandt S, Palandri F, Schröder N, Isermann B, Edlich F, Sinha AU, Ungelenk M, Hübner CA, Zeiser R, Rahmig S, Waskow C, Coldham I, Ernst T, Hochhaus A, Jilg S, Jost PJ, Mullally A, Bullinger L, Mertens PR, Lane SW, Mann M, Heidel FH
Nature 2020, 588(7836), 157-63 - Local and transient inhibition of p21 expression ameliorates age-related delayed wound healing.
Jiang D, de Vries JC, Muschhammer J, Schatz S, Ye H, Hein T, Fidan M, Romanov VS, Rinkevich Y, Scharffetter-Kochanek K
Wound Repair Regen 2020, 28(1), 49-60 - Staphylococcus aureus-Derived α-Hemolysin Evokes Generation of Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators Promoting Inflammation Resolution.
Jordan PM, Gerstmeier J, Pace S, Bilancia R, Rao Z, Börner F, Miek L, Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez Ó, Arakandy V, Rossi A, Ialenti A, González-Estévez C, Löffler B, Tuchscherr L, Serhan CN, Werz O
Cell Rep 2020, 33(2), 108247 - Correction: The acetyltransferase GCN5 maintains ATRA-resistance in non-APL AML.
Kahl M, Brioli A, Bens M, Perner F, Kresinsky A, Schnetzke U, Hinze A, Sbirkov Y, Stengel S, Simonetti G, Martinelli G, Petrie K, Zelent A, Böhmer FD, Groth M, Ernst T, Heidel FH, Scholl S, Hochhaus A, Schenk T
Leukemia 2020, 34(7), 1972