Subarea 1: Stem Cell Aging
The individual research groups within Subarea 1 investigate the causes and consequences of stem cell aging. The research work spans from basic model organisms over genetic mouse models up to humanized mouse models engrafted with human stem cells.
According to the FLI, with the closure of two groups since 2016 the representation of invertebrate models of stem cell research was reduced in Subarea 1. The institute presumes that the recruitment of new groups should fill this gap.
The research is defined by four focus areas:
- Cell-intrinsic mechanisms limiting the function of aging stem and progenitor cells,
- Aging-associated alterations of stem cell niches and the systemic environment,
- Mechanisms of clonal selection and epigenetic drifts in stem cell aging, and
- Microbiota- and metabolism-induced impairments in stem cell function during aging (in context of the new focus area Microbiota and Aging currently being built up within Subarea 2).
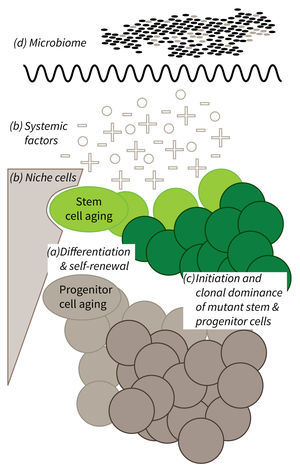
Research focus of Subarea 1.
a) It is currently not well understood what mechanisms impair cellular functions in aging. b) The relative contribution of niche cells and systemic acting factors on stem cell aging have yet to be determined in different tissues. c) Clonal expansion of mutant cells associates with disease development in aging humans. Mechanistically, the process remains poorly understood. Changes in color intensity depict clonal dominance originating from stem (green) or progenitor cells (gray). d) Emerging evidences indicate that aging associated alter ations in microbiota influence stem cell function and vice versa.
Publications
(since 2016)
2023
- IFNγ-Stat1 axis drives aging-associated loss of intestinal tissue homeostasis and regeneration.
Omrani* O, Krepelova* A, Rasa SMM, Sirvinskas D, Lu J, Annunziata F, Garside G, Bajwa S, Reinhardt S, Adam L, Käppel S, Ducano N, Donna D, Ori A, Oliviero S, Rudolph KL, Neri F
Nat Commun 2023, 14(1), 6109 * equal contribution - T Cells Expressing a Modified FcγRI Exert Antibody-Dependent Cytotoxicity and Overcome the Limitations of CAR T-cell Therapy against Solid Tumors.
Rasoulouniriana D, Santana-Magal N, Gutwillig A, Farhat-Younis L, Tal L, Amar S, Milyavsky M, Muddineni SSNA, Solomon N, Shpilt H, Dotan S, Pilpel N, Waskow C, Feinmesser M, Rider P, Carmi Y
CANCER IMMUNOL RES 2023, 11(6), 792 - Gene regulatory network inference with popInfer reveals dynamic regulation of hematopoietic stem cell quiescence upon diet restriction and aging.
Rommelfanger* MK, Behrends* M, Chen Y, Martinez J, Bens M, Xiong L, Rudolph** KL, MacLean** AL
bioRxiv 2023, https://www.doi.org/10.1101/2023 * equal contribution, ** co-corresponding authors - Dynamic DNA methylation reveals novel cis-regulatory elements in mouse hematopoiesis.
Schönung M, Hartmann M, Krämer S, Stäble S, Hakobyan M, Kleinert E, Aurich T, Cobanoglu D, Heidel FH, Fröhling S, Milsom MD, Schlesner M, Lutsik P, Lipka DB
Exp Hematol 2023, 117, 24-42.e7 - Cre recombinase expression cooperates with homozygous FLT3 internal tandem duplication knockin mouse model to induce acute myeloid leukemia.
Straube* J, Eifert* T, Vu T, Janardhanan Y, Haldar R, von Eyss B, Cooper L, Bruedigam C, Ling VY, Cooper E, Patch AM, Bullinger L, Schnoeder TM, Bywater M, Heidel* FH, Lane* SW
Leukemia 2023, 37(4), 741 * equal contribution - Immunoproteasome function maintains oncogenic gene expression in KMT2A-complex driven leukemia.
Tubío-Santamaría N, Jayavelu AK, Schnoeder TM, Eifert T, Hsu CJ, Perner F, Zhang Q, Wenge DV, Hansen FM, Kirkpatrick JM, Jyotsana N, Lane SW, von Eyss B, Deshpande AJ, Kühn MWM, Schwaller J, Cammann C, Seifert U, Ebstein F, Krüger E, Hochhaus A, Heuser M, Ori A, Mann M, Armstrong SA, Heidel FH
Mol Cancer 2023, 22(1), 196
2022
- Vitamin A metabolism in niche cells activates retinoic acid signaling and impairs stem cell function and skeletal muscle maintenance in aging mice
Becker F
Dissertation 2022, Jena - Impaired formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome.
Brings C, Fröbel J, Cadeddu RP, Germing U, Haas R, Gattermann N
BLOOD ADV 2022, 6(1), 129-37 - Combined Activity of the Redox-Modulating Compound Setanaxib (GKT137831) with Cytotoxic Agents in the Killing of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells.
Demircan MB, Mgbecheta PC, Kresinsky A, Schnoeder TM, Schröder K, Heidel FH, Böhmer FD
Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11(3), 513 - Context-specific effects of NOX4 inactivation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Demircan MB, Schnoeder TM, Mgbecheta PC, Schröder K, Böhmer FD, Heidel FH
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2022, 148(8), 1983-90