Subarea 1: Stem Cell Aging
The individual research groups within Subarea 1 investigate the causes and consequences of stem cell aging. The research work spans from basic model organisms over genetic mouse models up to humanized mouse models engrafted with human stem cells.
According to the FLI, with the closure of two groups since 2016 the representation of invertebrate models of stem cell research was reduced in Subarea 1. The institute presumes that the recruitment of new groups should fill this gap.
The research is defined by four focus areas:
- Cell-intrinsic mechanisms limiting the function of aging stem and progenitor cells,
- Aging-associated alterations of stem cell niches and the systemic environment,
- Mechanisms of clonal selection and epigenetic drifts in stem cell aging, and
- Microbiota- and metabolism-induced impairments in stem cell function during aging (in context of the new focus area Microbiota and Aging currently being built up within Subarea 2).
Research focus of Subarea 1.
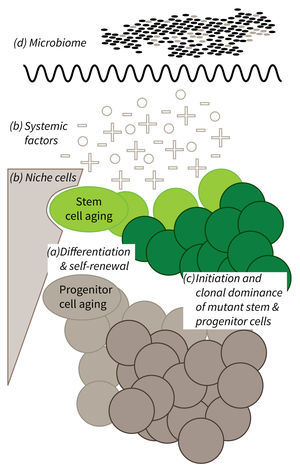
a) It is currently not well understood what mechanisms impair cellular functions in aging. b) The relative contribution of niche cells and systemic acting factors on stem cell aging have yet to be determined in different tissues. c) Clonal expansion of mutant cells associates with disease development in aging humans. Mechanistically, the process remains poorly understood. Changes in color intensity depict clonal dominance originating from stem (green) or progenitor cells (gray). d) Emerging evidences indicate that aging associated alter ations in microbiota influence stem cell function and vice versa.
Publications
(since 2016)
2021
- Regeneration in starved planarians depends on TRiC/CCT subunits modulating the unfolded protein response.
Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez* Ó, Felix* DA, Salvetti A, Amro EM, Thems A, Pietsch S, Koeberle A, Rudolph KL, González-Estévez C
EMBO Rep 2021, 22(8), e52905 * equal contribution - The Role of MacroH2A Histone Variants in Cancer.
Hsu CJ, Meers O, Buschbeck M, Heidel FH
Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13(12), 3003 - Therole of the transcriptional repressor TRPS1 in rhabdomyosarcoma and myogenesis
Hüttner S
Dissertation 2021, Jena, Germany - Single Myofiber Culture Assay for the Assessment of Adult Muscle Stem Cell Functionality Ex Vivo.
Hüttner SS, Hayn C, Ahrens HE, Schmidt M, Henze H, von Maltzahn J
J Vis Exp 2021, doi: 10.3791/62257 - Publisher Correction: SIRT7: an influence factor in healthy aging and the development of age-dependent myeloid stem-cell disorders.
Kaiser A, Schmidt M, Huber O, Frietsch JJ, Scholl S, Heidel FH, Hochhaus A, Müller JP, Ernst T
Leukemia 2021, 35(12), 3632 - Deletion of H2AX aggravates telomere dysfunction induced DNA damage and atrophy of the intestinal epithelium
Omrani O
Dissertation 2021, Jena, Germany - DNA-methylation aging at single-cell level
Rudolph KL
Nature Aging 2021, 1, 1086–1087 - Stem cell aging.
Rudolph KL
Mech Ageing Dev 2021, 193, 111394 - Stimulation of Non-canonical NF-κB Through Lymphotoxin-β-Receptor Impairs Myogenic Differentiation and Regeneration of Skeletal Muscle.
Schmidt M, Weidemann A, Poser C, Bigot A, von Maltzahn J
Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 721543 - Extensive remodeling of the extracellular matrix during aging contributes to age-dependent impairments of muscle stem cell functionality.
Schüler SC, Kirkpatrick* JM, Schmidt* M, Santinha D, Koch P, Di Sanzo S, Cirri E, Hemberg M, Ori** A, von Maltzahn** J
Cell Rep 2021, 35(10), 109223 * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors