Subarea 2: Regeneration and Homeostasis of Organs in Aging
The main goal of Subarea 2 is to identify cellular and molecular pathways used to ensure effective organ maintenance and repair, and to unravel the mechanisms of their deterioration during aging. While stem cells are important for organ homeostasis, this Subarea does not per se directly addresses stem cell aging but rather focusses on the following focus areas:
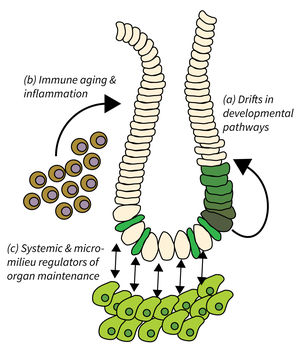
- Drifts in developmental pathways limiting organ maintenance in aging,
- Immune aging and inflammation, and
- Systemic and micro-milieu regulators of organ maintenance, regeneration, and disease development.
Research focus of Subarea 2
Organ maintenance is regulated by local and systemic factors, which are subject to aging-associated changes. Research of Subarea 2 focuses on the following research areas: a) Genetic and epigenetic modulation of developmental pathways has been shown to contribute to progressive aging and disease. It is critical to delineate mechanisms and consequences of aging-associated drifts to better understand organ maintenance during aging. b) Immunoaging and chronic inflammation elicits negative effects through reduced immune surveillance and aberrant organ repair and maintenance; all of which contributes to the evolution of organ pathologies and diseases during organismal aging. c) Furthermore, aging-associated alterations in systemic and extracellular factors derived from metabolic changes, microbiota alterations, chronic inflammation, senescent, or damaged cells might impinge on disease development and tumor initiation.
Publications
(since 2016)
2021
- The LIM domain protein nTRIP6 modulates the dynamics of myogenic differentiation.
Norizadeh Abbariki T, Gonda Z, Kemler D, Urbanek P, Wagner T, Litfin M, Wang ZQ, Herrlich P, Kassel O
Sci Rep 2021, 11(1), 12904 - Stimulation of Non-canonical NF-κB Through Lymphotoxin-β-Receptor Impairs Myogenic Differentiation and Regeneration of Skeletal Muscle.
Schmidt M, Weidemann A, Poser C, Bigot A, von Maltzahn J
Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 721543 - TRIP6 functions in brain ciliogenesis.
Shukla S, Haenold* R, Urbánek* P, Frappart L, Monajembashi S, Grigaravicius P, Nagel S, Min WK, Tapias A, Kassel O, Heuer H, Wang ZQ, Ploubidou** A, Herrlich** P
Nat Commun 2021, 12(1), 5887 * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors - A comprehensive transcriptome signature of murine hematopoietic stem cell aging.
Svendsen AF, Yang D, Kim KM, Lazare SS, Skinder N, Zwart E, Mura-Meszaros A, Ausema A, Eyss Bv, de Haan G, Bystrykh LV
Blood 2021, 138(6), 439-51 - Correction: Dietary restriction improves repopulation but impairs lymphoid differentiation capacity of hematopoietic stem cells in early aging.
Tang D, Tao S, Chen Z, Koliesnik IO, Calmes PG, Hoerr V, Han B, Gebert N, Zörnig M, Löffler B, Morita Y, Rudolph KL
J Exp Med 2021, 218(1), jem.2015110012042020C - Transcriptional Regulation
Tuckermann J, Herrlich P, Caratti G
In: Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology (edited by Stefan Offermanns and Walter Rosenthal) 2021, Springer International Publishin
2020
- The Peripheral Nervous System in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Aging.
Böhm L, Helbing DL, Oraha N, Morrison H
Mech Ageing Dev 2020, 191, 111329 - Optimization of blocking conditions for fluorescent Western blot.
Cui Y
Anal Biochem 2020, 593, 113598 - Control mechanisms of YAP activity
Elster D
Dissertation 2020, Jena, Germany - Hippo Signaling in Regeneration and Aging.
Elster D, von Eyss B
Mech Ageing Dev 2020, 189, 111280