Subarea 2: Regeneration and Homeostasis of Organs in Aging
The main goal of Subarea 2 is to identify cellular and molecular pathways used to ensure effective organ maintenance and repair, and to unravel the mechanisms of their deterioration during aging. While stem cells are important for organ homeostasis, this Subarea does not per se directly addresses stem cell aging but rather focusses on the following focus areas:
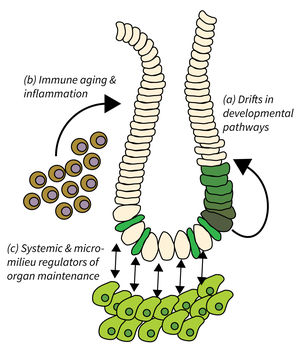
- Drifts in developmental pathways limiting organ maintenance in aging,
- Immune aging and inflammation, and
- Systemic and micro-milieu regulators of organ maintenance, regeneration, and disease development.
Research focus of Subarea 2
Organ maintenance is regulated by local and systemic factors, which are subject to aging-associated changes. Research of Subarea 2 focuses on the following research areas: a) Genetic and epigenetic modulation of developmental pathways has been shown to contribute to progressive aging and disease. It is critical to delineate mechanisms and consequences of aging-associated drifts to better understand organ maintenance during aging. b) Immunoaging and chronic inflammation elicits negative effects through reduced immune surveillance and aberrant organ repair and maintenance; all of which contributes to the evolution of organ pathologies and diseases during organismal aging. c) Furthermore, aging-associated alterations in systemic and extracellular factors derived from metabolic changes, microbiota alterations, chronic inflammation, senescent, or damaged cells might impinge on disease development and tumor initiation.
Publications
(since 2016)
2017
- Loss of menin in osteoblast lineage affects osteocyte-osteoclast crosstalk causing osteoporosis.
Liu P, Lee S, Knoll J, Rauch A, Ostermay S, Luther J, Malkusch N, Lerner UH, Zaiss MM, Neven M, Wittig R, Rauner M, David JP, Bertolino P, Zhang CX, Tuckermann JP
Cell Death Differ 2017, 24(4), 672-82 - Merlin controls the repair capacity of Schwann cells after injury by regulating Hippo/YAP activity.
Mindos T, Dun XP, North K, Doddrell RDS, Schulz A, Edwards P, Russell J, Gray B, Roberts SL, Shivane A, Mortimer G, Pirie M, Zhang N, Pan D, Morrison H, Parkinson DB
J Cell Biol 2017, 216(2), 495-510 - Vitamin A regulates Akt signaling through the phospholipid fatty acid composition.
Pein* H, Koeberle* SC, Voelkel M, Schneider F, Rossi A, Thürmer M, Loeser K, Sautebin L, Morrison H, Werz O, Koeberle A
FASEB J 2017, 31(10), 4566-77 * equal contribution - Central immune tolerance depends on crosstalk between the classical and alternative NF-κB pathways in medullary thymic epithelial cells.
Riemann M, Andreas N, Fedoseeva M, Meier E, Weih D, Freytag H, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Klein U, Wang ZQ, Weih F
J Autoimmun 2017, 81, 56-67 - Deletion of Gas2l3 in mice leads to specific defects in cardiomyocyte cytokinesis during development.
Stopp S, Gründl M, Fackler M, Malkmus J, Leone M, Naumann R, Frantz S, Wolf E, von Eyss B, Engel FB, Gaubatz S
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114(30), 8029-34 published during change of institution - RHEB1 insufficiency in aged male mice is associated with stress-induced seizures.
Tian Q, Gromov P, Clement JH, Wang Y, Riemann M, Weih F, Sun XX, Dai MS, Fedorov LM
Geroscience 2017, 39(5-6), 557-70 - Post-transcriptional control of C/EBPα and C/EBPβ proteins: Insights into their role in energy homeostasis and diseases
Zaini MA
Dissertation 2017, Groningen, Netherlands
2016
- RelB-dependent CD117+ CD172a+ cDCs induce Th2 cell responses and maintain RORϫt+ Treg homeostasis in mucosal tissues
Andreas N
Dissertation 2016, Jena, Germany - From the bush to the bench: the annual Nothobranchius fishes as a new model system in biology.
Cellerino A, Valenzano DR, Reichard M
Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 2016, 91(2), 511-33 - The role of hypothalamic NF-κB signaling in the response of the HPT-axis to acute inflammation in female mice.
de Vries EM, Nagel S, Haenold R, Sundaram SM, Pfrieger FW, Fliers E, Heuer H, Boelen A
Endocrinology 2016, 157(7), 2947-56