Subarea 3: Genetics and Epigenetics of Aging
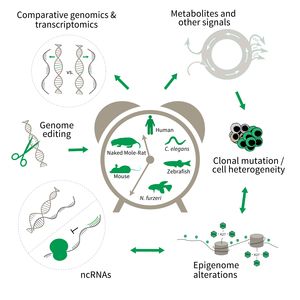
The focus of Subarea 3 is on genetic and epigenetic determinants of life- and health span as well as aging in fish, rodents and humans. This line of research builds on the expertise of the institute in comparative and functional genomics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Comparative genomics in short- and long-lived models of aging,
- Genomic engineering in N. furzeri,
- Epigenetics of aging,
- Non-coding RNAs in aging, and
- Comparative transcriptomics of aging.
Research focus of Subarea 3.
To uncover causative factors for aging, comparative genomics in short- and long-lived model systems are applied. Functional genomics is used to identify novel pathways contribute to aging of an organism and to validate the functional relevance of genetic and epigenetic changes that occur during aging. Furthermore, genetic risk factors for aging-related diseases are identified and functionally tested. The future development of the Subarea aims to integrate changes in host-microbiota interactions during aging, and how these influence clonal mutation and epigenetic alterations through metabolites and other signals.
Publications
(since 2016)
2022
- Single-cell atlas of the aging mouse colon.
Širvinskas D, Omrani O, Lu J, Rasa M, Krepelova A, Adam L, Kaeppel S, Sommer F, Neri F
iScience 2022, 25(5), 104202 - A genome-wide CRISPR activation screen reveals Hexokinase 1 as a critical factor in promoting resistance to multi-kinase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Sofer S, Lamkiewicz K, Armoza Eilat S, Partouche S, Marz M, Moskovits N, Stemmer SM, Shlomai A, Sklan EH
FASEB J 2022, 36(3), e22191 - Sex chromosome differentiation via changes in the Y chromosome repeat landscape in African annual killifishes Nothobranchius furzeri and N. kadleci.
Štundlová J, Hospodářská M, Lukšíková K, Voleníková A, Pavlica T, Altmanová M, Richter A, Reichard M, Dalíková M, Pelikánová Š, Marta A, Simanovsky SA, Hiřman M, Jankásek M, Dvořák T, Bohlen J, Ráb P, Englert C, Nguyen P, Sember A
Chromosome Res 2022, 30(4), 309-33 - The Mating Pattern of Captive Naked Mole-Rats Is Best Described by a Monogamy Model
Szafranski* K, Wetzel* M, Holtze S, Büntjen I, Lieckfeldt D, Ludwig A, Huse K, Platzer M, Hildebrandt T
FRONT ECOL EVOL 2022, 10, 855688 * equal contribution - Characterization of RNA content in individual phase-separated coacervate microdroplets.
Wollny D, Vernot B, Wang J, Hondele M, Safrastyan A, Aron F, Micheel J, He Z, Hyman A, Weis K, Camp JG, Tang TYD, Treutlein B
Nat Commun 2022, 13(1), 2626 - The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in the Human Placenta.
Žarković* M, Hufsky* F, Markert** UR, Marz** M
Cells 2022, 11(9), 1588 * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors
2021
- Analysis of intestinal stem cell competition in calorie restriction and aging
Annunziata F
Dissertation 2021, Jena - Analysis of microRNA expression reveals convergent evolution of the molecular control of diapause in annual fish
Barth E, Baumgart M, Dolfi L, Cui R, Groth M, Ripa R, Savino A, R.Valenzano D, Marz M, Cellerino A
Research Square 2021, https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs - Age-dependent expression changes of circadian system-related genes reveal a potentially conserved link to aging.
Barth E, Srivastava A, Wengerodt D, Stojiljkovic M, Axer H, Witte OW, Kretz** A, Marz** M
Aging (Albany NY) 2021, 13(24), 25694-716 - Antithetic hTERT Regulation by Androgens in Prostate Cancer Cells: hTERT Inhibition Is Mediated by the ING1 and ING2 Tumor Suppressors.
Bartsch S, Mirzakhani K, Neubert L, Stenzel A, Ehsani M, Esmaeili M, Pungsrinont T, Kacal M, Rasa SMM, Kallenbach J, Damodaran D, Ribaudo F, Grimm MO, Neri F, Baniahmad A
Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13(16), 4025