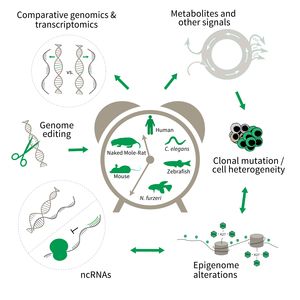
Subarea 3: Genetics and Epigenetics of Aging
The focus of Subarea 3 is on genetic and epigenetic determinants of life- and health span as well as aging in fish, rodents and humans. This line of research builds on the expertise of the institute in comparative and functional genomics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Comparative genomics in short- and long-lived models of aging,
- Genomic engineering in N. furzeri,
- Epigenetics of aging,
- Non-coding RNAs in aging, and
- Comparative transcriptomics of aging.
Research focus of Subarea 3.
To uncover causative factors for aging, comparative genomics in short- and long-lived model systems are applied. Functional genomics is used to identify novel pathways contribute to aging of an organism and to validate the functional relevance of genetic and epigenetic changes that occur during aging. Furthermore, genetic risk factors for aging-related diseases are identified and functionally tested. The future development of the Subarea aims to integrate changes in host-microbiota interactions during aging, and how these influence clonal mutation and epigenetic alterations through metabolites and other signals.
Publications
(since 2016)
2023
- Characterization of myc mutants in the short-lived killifish Nothobranchius furzeri
Zhang Z
Dissertation 2023, Jena, Germany
2022
- Paneth cells drive intestinal stem cell competition and clonality in aging and calorie restriction
Annunziata F, Rasa SMM, Krepelova A, Lu J, Minetti A, Omrani O, Nunna S, Adam L, Käppel S, Neri F
Eur J Cell Biol 2022, 101(4), 151282 - Quantification of noradrenergic-, dopaminergic-, and tectal-neurons during aging in the short-lived killifish Nothobranchius furzeri.
Bagnoli S, Fronte B, Bibbiani C, Terzibasi Tozzini E, Cellerino A
Aging Cell 2022, 21(9), e13689 - The natural compound atraric acid suppresses androgen-regulated neo-angiogenesis of castration-resistant prostate cancer through angiopoietin 2.
Ehsani M, Bartsch S, Rasa SMM, Dittmann J, Pungsrinont T, Neubert L, Huettner SS, Kotolloshi R, Schindler K, Ahmad A, Mosig AS, Adam L, Ori A, Neri F, Berndt A, Grimm MO, Baniahmad A
Oncogene 2022, 41(23), 3263-77 - Preface to Current Topics in Cellular Aging
Englert C
In: Current Topics in Cellular Aging, Selected articles published by MDPI, Cells 2022, MDPI - Multidisciplinary Digital - A deep neural network provides an ultraprecise multi-tissue transcriptomic clock for the short-lived fish Nothobranchius furzeri and identifies predicitive genes translatable to human aging
Ferrari E, Reichwald K, Koch P, Groth M, Baumgart M, Cellerino A
bioRxiv 2022, doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.26.51761 - Dogs as carriers of virulent and resistant genotypes of Clostridioides difficile.
Finsterwalder SK, Loncaric I, Cabal A, Szostak MP, Barf LM, Marz M, Allerberger F, Burgener IA, Tichy A, Feßler AT, Schwarz S, Monecke S, Ehricht R, Ruppitsch W, Spergser J, Künzel F
ZOONOSES PUBLIC HLTH 2022, 69(6), 673-81 - Comparative study of ten thogotovirus isolates and their distinct in vivo characteristics.
Fuchs J, Lamkiewicz K, Kolesnikova L, Hölzer M, Marz M, Kochs G
J Virol 2022, 96(5), e0155621 - The Wilms Tumor Gene wt1a Contributes to Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier Function in Zebrafish.
Hopfenmüller* VL, Perner* B, Reuter H, Bates TJD, Große A, Englert C
Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 9, 809962 * equal contribution - Epigenetic stress response during dietary restriction in ageing intestine
Husak O
Dissertation 2022, Jena, Germany