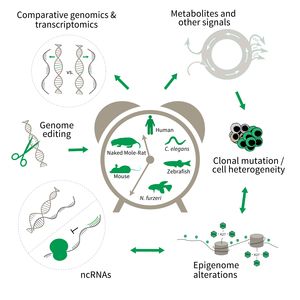
Subarea 3: Genetics and Epigenetics of Aging
The focus of Subarea 3 is on genetic and epigenetic determinants of life- and health span as well as aging in fish, rodents and humans. This line of research builds on the expertise of the institute in comparative and functional genomics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Comparative genomics in short- and long-lived models of aging,
- Genomic engineering in N. furzeri,
- Epigenetics of aging,
- Non-coding RNAs in aging, and
- Comparative transcriptomics of aging.
Research focus of Subarea 3.
To uncover causative factors for aging, comparative genomics in short- and long-lived model systems are applied. Functional genomics is used to identify novel pathways contribute to aging of an organism and to validate the functional relevance of genetic and epigenetic changes that occur during aging. Furthermore, genetic risk factors for aging-related diseases are identified and functionally tested. The future development of the Subarea aims to integrate changes in host-microbiota interactions during aging, and how these influ ence clonal mutation and epigenetic alterations through metabolites and other signals.
Publications
(since 2016)
2021
- Mechanistic insights into p53-regulated cytotoxicity of combined entinostat and irinotecan against colorectal cancer cells.
Marx C, Sonnemann J, Beyer M, Maddocks ODK, Lilla S, Hauzenberger I, Piée-Staffa A, Siniuk K, Nunna S, Marx-Blümel L, Westermann M, Wagner T, Meyer FB, Thierbach R, Mullins CS, Kdimati S, Linnebacher M, Neri F, Heinzel T, Wang ZQ, Krämer OH
Mol Oncol 2021, 15(12), 3404-29 - A Novel Splice Variant of the Inhibitor of Growth 3 Lacks the Plant Homeodomain and Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Prostate Cancer Cells.
Melekhova A, Leeder M, Pungsrinont T, Schmäche T, Kallenbach J, Ehsani M, Mirzakhani K, Rasa SMM, Neri F, Baniahmad A
Biomolecules 2021, 11(8), 1152 - VIDHOP, viral host prediction with Deep Learning.
Mock F, Viehweger A, Barth E, Marz M
Bioinformatics 2021, 37(3), 318-25 - Rates of primary production in groundwater rival those in oligotrophic marine systems
Overholt WA, Trumbore S, Xu X, Bornemann TLV, Probst AJ, Krüger M, Herrmann M, Thamdrup B, Bristow L, Taubert M, Schwab VF, Hölzer M, Marz M, Küsel K
bioRxiv 2021, https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10. - Characterization of the transcriptome, the epigenome, and the microbiome during aging : dietary restriction ameliorates inflammaging
Rasa SMM
Dissertation 2021, Jena, Germany - Increased longevity due to sexual activity in mole-rats is associated with transcriptional changes in HPA stress axis.
Sahm* A, Platzer M, Koch P, Henning Y, Bens M, Groth M, Burda H, Begall S, Ting S, Goetz M, Van Daele P, Staniszewska M, Klose J, Costa PF, Hoffmann** S, Szafranski** K, Dammann** P
Elife 2021, 10, e57843 ** co-senior authors, * corresponding author - TRIP6 functions in brain ciliogenesis.
Shukla S, Haenold* R, Urbánek* P, Frappart L, Monajembashi S, Grigaravicius P, Nagel S, Min WK, Tapias A, Kassel O, Heuer H, Wang ZQ, Ploubidou** A, Herrlich** P
Nat Commun 2021, 12(1), 5887 * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors - HAT cofactor TRRAP modulates microtubule dynamics via SP1 signaling to prevent neurodegeneration.
Tapias* A, Lázaro* D, Yin* BK, Rasa SMM, Krepelova A, Kelmer Sacramento E, Grigaravicius P, Koch P, Kirkpatrick J, Ori A, Neri F, Wang ZQ
Elife 2021, 10, e61531 * equal contribution - DNA methylation modulates allograft survival and acute rejection after renal transplantation by regulating the mTOR pathway
Zhu C, Xiang W, Li B, Wang Y, Feng S, Wang C, Chen Y, Xie W, Qu L, Huang H, Annunziata F, Nunna S, Krepelova A, Rasa SMM, Neri F, Chen J, Jiang H
Am J Transplant 2021, 21(2), 567-81
2020
- NR2F1 regulates regional progenitor dynamics in the mouse neocortex and cortical gyrification in BBSOAS patients.
Bertacchi M, Romano AL, Loubat A, Tran Mau-Them F, Willems M, Faivre L, Khau van Kien P, Perrin L, Devillard F, Sorlin A, Kuentz P, Philippe C, Garde A, Neri F, Di Giaimo R, Oliviero S, Cappello S, D'Incerti L, Frassoni C, Studer M
EMBO J 2020, 39(13), e104163