Subarea 3: Genetics and Epigenetics of Aging
The focus of Subarea 3 is on genetic and epigenetic determinants of life- and health span as well as aging in fish, rodents and humans. This line of research builds on the expertise of the institute in comparative and functional genomics.
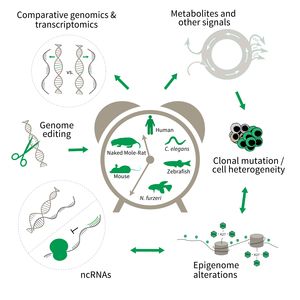
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Comparative genomics in short- and long-lived models of aging,
- Genomic engineering in N. furzeri,
- Epigenetics of aging,
- Non-coding RNAs in aging, and
- Comparative transcriptomics of aging.
Research focus of Subarea 3.
To uncover causative factors for aging, comparative genomics in short- and long-lived model systems are applied. Functional genomics is used to identify novel pathways contribute to aging of an organism and to validate the functional relevance of genetic and epigenetic changes that occur during aging. Furthermore, genetic risk factors for aging-related diseases are identified and functionally tested. The future development of the Subarea aims to integrate changes in host-microbiota interactions during aging, and how these influence clonal mutation and epigenetic alterations through metabolites and other signals.
Publications
(since 2016)
2020
- Reduced proteasome activity in the aging brain results in ribosome stoichiometry loss and aggregation.
Kelmer Sacramento* E, Kirkpatrick* JM, Mazzetto* M, Baumgart M, Bartolome A, Di Sanzo S, Caterino C, Sanguanini M, Papaevgeniou N, Lefaki M, Childs D, Bagnoli S, Terzibasi Tozzini E, Di Fraia D, Romanov N, Sudmant PH, Huber W, Chondrogianni N, Vendruscolo M, Cellerino** A, Ori** A
Mol Syst Biol 2020, 16(6), e9596 * equal contribution, ** co-corresponding authors - Der Türkise Prachtgrundkärpfling – ein Leben im Zeitraffer
Krug J, Richter A, Reuter H, Englert C
BIOspektrum 2020, 26, 375-77 - ADAM10 mediates ectopic proximal tubule development and renal fibrosis through Notch signalling.
Li B, Zhu C, Dong L, Qin J, Xiang W, Davidson AJ, Feng S, Wang Y, Shen X, Weng C, Wang C, Zhu T, Teng L, Wang J, Englert C, Chen J, Jiang H
J Pathol 2020, 252(3), 274-89 - Biomimetic reconstruction of the hematopoietic stem cell niche for in vitro amplification of human hematopoietic stem cells.
Marx-Blümel L, Marx C, Weise F, Frey J, Perner B, Schlingloff G, Lindig N, Hampl J, Sonnemann J, Brauer D, Voigt A, Singh S, Beck B, Jäger UM, Wang ZQ, Beck JF, Schober A
PLoS One 2020, 15(6), e0234638 - Ontogenetic Pattern Changes of Nucleobindin-2/Nesfatin-1 in the Brain and Intestinal Bulb of the Short Lived African Turquoise Killifish.
Montesano* A, Felice* ED, Leggieri A, Palladino A, Lucini C, Scocco P, Girolamo Pd, Baumgart** M, D'Angelo** L
J Clin Med 2020, 9(1), 103 * equal contribution, ** co-corresponding authors - A comprehensive annotation and differential expression analysis of short and long non-coding RNAs in 16 bat genomes.
Mostajo NF, Lataretu M, Krautwurst S, Mock F, Desirò D, Lamkiewicz K, Collatz M, Schoen A, Weber F, Marz M, Hölzer M
NAR Genom Bioinform 2020, 2(1), lqz006 - MiR-29 coordinates age-dependent plasticity brakes in the adult visual cortex.
Napoli D, Lupori L, Mazziotti R, Sagona G, Bagnoli S, Samad M, Sacramento EK, Kirkpartick J, Putignano E, Chen S, Terzibasi Tozzini E, Tognini P, Baldi P, Kwok JC, Cellerino* A, Pizzorusso* T
EMBO Rep 2020, 21(11), e50431 * equal contribution - Inclusion of Oxford Nanopore long reads improves all microbial and viral metagenome-assembled genomes from a complex aquifer system.
Overholt WA, Hölzer M, Geesink P, Diezel C, Marz M, Küsel K
Environ Microbiol 2020, 22(9), 4000-13 - A virtual "Werkstatt" for digitization in the sciences
Samuel S, Shadaydeh M, Böcker S, Brügmann B, Bucher SF, Deckert V, Denzler J, Dittrich P, Eggeling F, Güllmar D, Guntinas-Lichius O, König-Ries B, Löffler F, Maicher L, Marz M, Migliavacca M, Reichenbach JR, Reichstein M, Römermann C, Wittig A
Res Ideas Outcomes 2020, 6, e54106 - Wt1 Positive dB4 Neurons in the Hindbrain Are Crucial for Respiration
Schnerwitzki* D, Hayn* C, Perner B, Englert C
Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 529487 * equal contribution