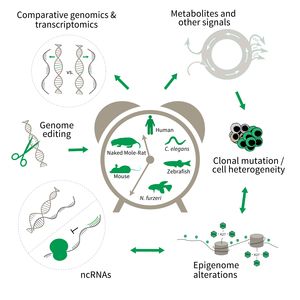
Subarea 3: Genetics and Epigenetics of Aging
The focus of Subarea 3 is on genetic and epigenetic determinants of life- and health span as well as aging in fish, rodents and humans. This line of research builds on the expertise of the institute in comparative and functional genomics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Comparative genomics in short- and long-lived models of aging,
- Genomic engineering in N. furzeri,
- Epigenetics of aging,
- Non-coding RNAs in aging, and
- Comparative transcriptomics of aging.
Research focus of Subarea 3.
To uncover causative factors for aging, comparative genomics in short- and long-lived model systems are applied. Functional genomics is used to identify novel pathways contribute to aging of an organism and to validate the functional relevance of genetic and epigenetic changes that occur during aging. Furthermore, genetic risk factors for aging-related diseases are identified and functionally tested. The future development of the Subarea aims to integrate changes in host-microbiota interactions during aging, and how these influ ence clonal mutation and epigenetic alterations through metabolites and other signals.
Publications
(since 2016)
2019
- TFEB controls vascular development by regulating the proliferation of endothelial cells.
Doronzo G, Astanina E, Corà D, Chiabotto G, Comunanza V, Noghero A, Neri F, Puliafito A, Primo L, Spampanato C, Settembre C, Ballabio A, Camussi G, Oliviero S, Bussolino F
EMBO J 2019, 38(3), e98250 - A CRISPR Activation Screen Identifies Genes That Protect against Zika Virus Infection.
Dukhovny A, Lamkiewicz K, Chen Q, Fricke M, Jabrane-Ferrat N, Marz M, Jung JU, Sklan EH
J Virol 2019, 93(16), e00211-19 - Global importance of RNA secondary structures in protein coding sequences.
Fricke M, Gerst R, Ibrahim B, Niepmann M, Marz M
Bioinformatics 2019, 35(4), 579-83 - Zebrafish Wtx is a negative regulator of Wnt signaling but is dispensable for embryonic development and organ homeostasis.
Große A, Perner B, Naumann U, Englert C
Dev Dyn 2019, 248(9), 866-81 - De novo transcriptome assembly: A comprehensive cross-species comparison of short-read RNA-Seq assemblers.
Hölzer M, Marz M
Gigascience 2019, 8(5), giz039 - Publisher Correction: Transcriptomic alterations during ageing reflect the shift from cancer to degenerative diseases in the elderly.
Irizar PA, Schäuble S, Esser D, Groth M, Frahm C, Priebe S, Baumgart M, Hartmann N, Marthandan S, Menzel U, Müller J, Schmidt S, Ast V, Caliebe A, König R, Krawczak M, Ristow M, Schuster S, Cellerino A, Diekmann S, Englert C, Hemmerich P, Sühnel J, Guthke R, Witte OW, Platzer M, Ruppin E, Kaleta C
Nat Commun 2019, 10(1), 2459 - The nuclear pore proteins Nup88/214 and T-ALL-associated NUP214 fusion proteins regulate Notch signaling.
Kindermann B, Valkova C, Krämer A, Perner B, Engelmann C, Behrendt L, Kritsch D, Jungnickel B, Kehlenbach RH, Oswald F, Englert C, Kaether C
J Biol Chem 2019, 294(31), 11741-50 - IMP dehydrogenase-2 drives aberrant nucleolar activity and promotes tumorigenesis in glioblastoma.
Kofuji S, Hirayama A, Eberhardt AO, Kawaguchi R, Sugiura Y, Sampetrean O, Ikeda Y, Warren M, Sakamoto N, Kitahara S, Yoshino H, Yamashita D, Sumita K, Wolfe K, Lange L, Ikeda S, Shimada H, Minami N, Malhotra A, Morioka S, Ban Y, Asano M, Flanary VL, Ramkissoon A, Chow LML, Kiyokawa J, Mashimo T, Lucey G, Mareninov S, Ozawa T, Onishi N, Okumura K, Terakawa J, Daikoku T, Wise-Draper T, Majd N, Kofuji K, Sasaki M, Mori M, Kanemura Y, Smith EP, Anastasiou D, Wakimoto H, Holland EC, Yong WH, Horbinski C, Nakano I, DeBerardinis RJ, Bachoo RM, Mischel PS, Yasui W, Suematsu M, Saya H, Soga T, Grummt I, Bierhoff H, Sasaki AT
Nat Cell Biol 2019, 21(8), 1003-14 - Identification and Expression of Neurotrophin-6 in the Brain of Nothobranchius furzeri: One More Piece in Neurotrophin Research.
Leggieri A, Attanasio C, Palladino A, Cellerino A, Lucini C, Paolucci M, Terzibasi Tozzini E, de Girolamo P, D'Angelo L
J Clin Med 2019, 8(5), 595 - Age-related central regulation of orexin and NPY in the short lived African killifish Nothobranchius furzeri.
Montesano* A, Baumgart* M, Avallone L, Castaldo L, Lucini C, Terzibasi Tozzini E, Cellerino** A, D'Angelo** L, de Girolamo** P
J Comp Neurol 2019, 527(9), 1508-26 * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors