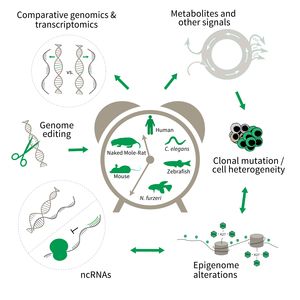
Subarea 3: Genetics and Epigenetics of Aging
The focus of Subarea 3 is on genetic and epigenetic determinants of life- and health span as well as aging in fish, rodents and humans. This line of research builds on the expertise of the institute in comparative and functional genomics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Comparative genomics in short- and long-lived models of aging,
- Genomic engineering in N. furzeri,
- Epigenetics of aging,
- Non-coding RNAs in aging, and
- Comparative transcriptomics of aging.
Research focus of Subarea 3.
To uncover causative factors for aging, comparative genomics in short- and long-lived model systems are applied. Functional genomics is used to identify novel pathways contribute to aging of an organism and to validate the functional relevance of genetic and epigenetic changes that occur during aging. Furthermore, genetic risk factors for aging-related diseases are identified and functionally tested. The future development of the Subarea aims to integrate changes in host-microbiota interactions during aging, and how these influ ence clonal mutation and epigenetic alterations through metabolites and other signals.
Publications
(since 2016)
2017
- DNMT and HDAC inhibitors induce cryptic transcription start sites encoded in long terminal repeats.
Brocks D, Schmidt CR, Daskalakis M, Jang HS, Shah NM, Li D, Li J, Zhang B, Hou Y, Laudato S, Lipka DB, Schott J, Bierhoff H, Assenov Y, Helf M, Ressnerova A, Islam MS, Lindroth AM, Haas S, Essers M, Imbusch CD, Brors B, Oehme I, Witt O, Lübbert M, Mallm JP, Rippe K, Will R, Weichenhan D, Stoecklin G, Gerhäuser C, Oakes CC, Wang T, Plass C
Nat Genet 2017, 49(7), 1052-60 published during change of institution - Renal regenerative potential of different extra-cellular vesicle populations derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells.
Bruno S, Tapparo M, Collino F, Chiabotto G, Deregibus MC, Soares Lindoso R, Neri F, Kholia S, Giunti S, Wen S, Quesenberry P, Camussi G
TISSUE ENG PART A 2017, 23(21-22), 1262-73 - What have we learned on aging from omics studies?
Cellerino A, Ori A
Semin Cell Dev Biol 2017, 70, 177-89 - Endogenous locus-driven H-Ras G12V expression induces senescence-like phenotype in primary fibroblasts of the Costello syndrome mouse model
Chennappan S, Schulze T, Cirstea IC
Molecular Life 2017, 1(1), 3-14 - Genetic mutations linked to Parkinson's disease differentially control nucleolar activity in pre-symptomatic mouse models.
Evsyukov V, Domanskyi A, Bierhoff H, Gispert S, Mustafa R, Schlaudraff F, Liss B, Parlato R
Dis Model Mech 2017, 10(5), 633-43 - Transcriptional profiling reveals protective mechanisms in brains of long-lived mice.
Frahm C, Srivastava A, Schmidt S, Mueller J, Groth M, Guenther M, Ji Y, Priebe S, Platzer M, Witte OW
Neurobiol Aging 2017, 52, 23-31 - Evolution and antiviral specificity of interferon-induced Mx proteins of bats against Ebola-, Influenza-, and other RNA viruses.
Fuchs J, Hölzer M, Schilling M, Patzina C, Schoen A, Hoenen T, Zimmer G, Marz M, Weber F, Müller MA, Kochs G
J Virol 2017, 91(15), e00361-17 - microRNA-122 target sites in the hepatitis C virus RNA NS5B coding region and 3' untranslated region: function in replication and influence of RNA secondary structure.
Gerresheim GK, Dünnes N, Nieder-Röhrmann A, Shalamova LA, Fricke M, Hofacker I, Höner Zu Siederdissen C, Marz M, Niepmann M
Cell Mol Life Sci 2017, 74(4), 747-60 - Age-dependent increase of oxidative stress regulates microRNA-29 family preserving cardiac health.
Heid* J, Cencioni* C, Ripa* R, Baumgart* M, Atlante S, Milano G, Scopece A, Kuenne C, Guenther S, Azzimato V, Farsetti A, Rossi G, Braun T, Pompilio G, Martelli F, Zeiher AM, Cellerino** A, Gaetano** C, Spallotta** F
Sci Rep 2017, 7(1), 16839 * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors - Software Dedicated to Virus Sequence Analysis "Bioinformatics Goes Viral".
Hölzer M, Marz M
In: Advances in Virus Research (edited by Beer M, Höper D) 2017, 99, 233-257, Academic Press, London