Subarea 4: Cell Dynamics and Molecular Damages in Aging
The research focus of Subarea 4 is on studying damages of macromolecules (proteins, nucleic acids) and determining the structure-function relationship of biomolecules relevant to damage and damage repair processes and responses to molecular damage that might lead to aging and aging-associated pathologies.
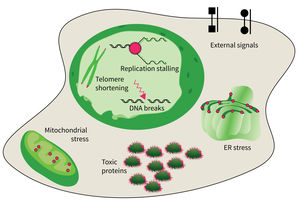
The studies are focused on the following research areas: DNA replication, DNA damage responses (DDR), stress responses, metabolic stresses, protein trafficking and protein damages.
The research is defined by four focus areas:
- DNA damage response in tissue homeostasis and neuropathies,
- Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum for secretory pathway in aging processes,
- Intrinsic and extrinsic factors implicated in cellular decline during aging, and
- DNA replication and genomic integrity preventing premature aging and diseases.
Research focus of Subarea 4.
The accumulation of damaged macromolecules or subcellular organelles is associated with dysfunction of a cell, which contributes to tissue & organ failure. DNA damage, genomic instability, protein misfolding or defects in toxic protein degradation can compromise cell functionality. Alterations of mitochondrial DNA and protein complexes affect cellular metabolism, which will have a general impact on cell integrity.
Publications
(since 2016)
2019
- In vivo Study of Human DHX9 Helicase Functions
Aly YSH
Dissertation 2019, Jena, Germany - A disease causing ATLASTIN 3 mutation affects multiple endoplasmic reticulum-related pathways.
Behrendt L, Kurth I, Kaether C
Cell Mol Life Sci 2019, 76(7), 1433-45 - BRCA1 mislocalization leads to aberrant DNA damage response in heterozygous ABRAXAS1 mutation carrier cells.
Bose M, Sachsenweger J, Laurila N, Parplys AC, Willmann J, Jungwirth J, Groth M, Rapakko K, Nieminen P, Friedl TWP, Heiserich L, Meyer F, Tuppurainen H, Peltoketo H, Nevanlinna H, Pylkäs K, Borgmann K, Wiesmüller L, Winqvist** R, Pospiech** H
Hum Mol Genet 2019, 28(24), 4148-60 ** co-corresponding authors - Early-life Pb exposure as a potential risk factor for Alzheimer's disease: are there hazards for the Mexican population?
Chin-Chan M, Cobos-Puc L, Alvarado-Cruz I, Bayar M, Ermolaeva M
J Biol Inorg Chem 2019, 24(8), 1285-303 - It is not all about regeneration: planarians striking power to stand starvation.
Felix DA, Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez Ó, Espada L, Thems A, González-Estévez C
Semin Cell Dev Biol 2019, 87, 169-81 - Publisher Correction: Transcriptomic alterations during ageing reflect the shift from cancer to degenerative diseases in the elderly.
Irizar PA, Schäuble S, Esser D, Groth M, Frahm C, Priebe S, Baumgart M, Hartmann N, Marthandan S, Menzel U, Müller J, Schmidt S, Ast V, Caliebe A, König R, Krawczak M, Ristow M, Schuster S, Cellerino A, Diekmann S, Englert C, Hemmerich P, Sühnel J, Guthke R, Witte OW, Platzer M, Ruppin E, Kaleta C
Nat Commun 2019, 10(1), 2459 - The Enigmatic Function of PARP1: From PARylation Activity to PAR Readers.
Kamaletdinova* T, Fanaei-Kahrani* Z, Wang ZQ
Cells 2019, 8(12) - Age effect on thyroid hormone brain response in male mice.
Kerp H, Engels K, Kramer F, Doycheva D, Sebastian Hönes G, Zwanziger D, Christian Moeller L, Heuer H, Führer D
Endocrine 2019, 66(3), 596-606 - The nuclear pore proteins Nup88/214 and T-ALL-associated NUP214 fusion proteins regulate Notch signaling.
Kindermann B, Valkova C, Krämer A, Perner B, Engelmann C, Behrendt L, Kritsch D, Jungnickel B, Kehlenbach RH, Oswald F, Englert C, Kaether C
J Biol Chem 2019, 294(31), 11741-50 - Analysis of conditional Rer1 knockout mice
Klare S
Dissertation 2019, Jena, Germany