Jena. Researchers at the Leibniz Institute on Aging - Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI) in Jena have discovered a new function of the DNA repair protein ATR in regulating mitochondria homeostasis. This discovery makes a significant contribution to understanding the etiology of Genomic Instability Diseases, such as Seckel Syndrome. The study, entitled "DNA damage response regulator ATR licenses PINK1-mediated mitophagy," has been published in the renowned journal Nucleic Acids Research. Dr. Christian Marx, from the Wang research group, is the first author of the study. Professor Dr. Zhao-Qi Wang is an Emeritus Senior Group Leader at the FLI and now conducting research at Shandong University in China.
The results of the new study are surprising: the protein ATR, previously known primarily for its role in DNA damage response, apparently also plays a crucial role in regulating mitochondria fitness, which has a general function in maintaining tissue homeostasis and healthy aging. ATR ensures that the cell does not continue to grow when DNA is damaged by activating cellular checkpoint. Mutations in ATR lead to human disease Seckel syndrome, characterized by dwarfism, microcephaly, intellectual disability, and premature aging.
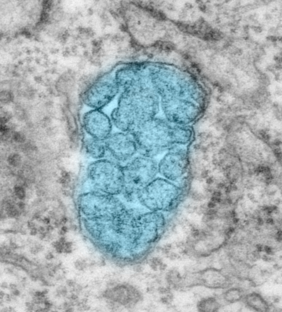
The new function of ATR involves its localization not only in the nucleus but also in mitochondria, the "powerhouses" of the cell. ATR interacts with PINK1, the key regulator of the mitochondrial quality control program, namely mitophagy, a process in which damaged mitochondria are cleaned, protecting cells from detrimental effects of sick mitochondria. Without ATR PINK1-mediated mitophagy is silenced.
The discovery of the new function of ATR in the mitochondrial quality control program is important, because it helps to understand the etiology of Genomic Instability Syndromes, neurodegenerative diseases as well as premature aging. This discovery could open up new approaches for treating these diseases.
Highlights of the study
- ATR is localized at mitochondria and interacts with PINK1 to regulate the mitochondrial quality control program.
- ATR inspects the genomic and mitochondrial integrity and safeguards the tissue homeostasis under physiological and genotoxic conditions.
- The discovery of the new function of ATR in mitophagy provides insights into the physiological function of a DNA damage response regulator in neuropathies and tissue declines, as well as the aging process.
- The study could open up new approaches for treating diseases such as Seckel syndrome and other neurodegenerative conditions, e.g., by enforcing the mitochondrial quality control program or by scavenging reactive oxygen species originating from sick mitochondria.
Publication
DNA damage response regulator ATR licenses PINK1-mediated mitophagy. Marx C, Qing X, Gong Y, Kirkpatrick J, Siniuk K, Beznoussenko GV, Kidiyoor GR, Kirtay M, Buder K, Koch P, Westermann M, Bruhn C, Brown EJ, Xu X, Foiani M, Wang ZQ. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53(5), gkaf178. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf178.
Contact
Sylvia Kreyssel-Minar
Phone: +49 3641-65-6378
Email: presse@leibniz-fli.de