Subarea 5: Computational and Systems Biology of Aging
Subarea 5 focuses on the development of methods to analyse and understand complex biological systems. This work includes the design of computer algorithms and biostatistical approaches as well as the development of novel Omic strategies (i.e. genomics/epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) to study aging and aging-related diseases. According to the FLI, due to the Subarea's expertise in computational data analysis, it is deeply interconnected with all other Subareas. The Subarea hosts two critical core facilities (Life Science Computing, Proteomics) and provides consulting services in statistics. Furthermore, it organizes courses on data analysis and statistics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Mapping extrinsic and intrinsic factors influencing stem cells during aging,
- Integration of spatiotemporal proteomics and transcriptomics data,
- Comprehensive evaluation of qualitative and quantitative expression changes,
- Identification and analysis of epigenomic alterations during aging and age-related diseases, and
- Network analysis of genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic alterations during aging.
Research focus of Subarea 5.
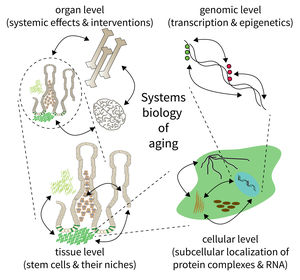
The biology of aging can be viewed as a multilayered array of networks at the level of organs, cells, molecules, and genes. The FLI wants to meet this complexity by establishing the new Subarea on “Computational and Systems Biology of Aging”. The overall goal is to interconnect research at different scales, taking place in Subareas 1-4 of the Institute’s research program. The new group on Systems Biology will integrate data from networks at multiple scales and will thus point to mechanisms and interactions that would not be seen in unilayer approaches.
Publications
(since 2016)
2025
- Integrative multiomic approaches reveal ZMAT3 and p21 as conserved hubs in the p53 tumor suppression network.
Boutelle AM, Mabene AR, Yao D, Xu H, Wang M, Tang YJ, Lopez SS, Sinha S, Demeter J, Cheng R, Benard BA, McCrea EM, Valente LJ, Drainas AP, Fischer M, Majeti R, Petrov DA, Jackson PK, Yang F, Winslow MM, Bassik MC, Attardi LD
Cell Death Differ 2025 (epub ahead of print) - Rapid brain tumor classification from sparse epigenomic data.
Brändl B, Steiger M, Kubelt C, Rohrandt C, Zhu Z, Evers M, Wang G, Schuldt B, Afflerbach AK, Wong D, Lum A, Halldorsson S, Djirackor L, Leske H, Magadeeva S, Smičius R, Quedenau C, Schmidt NO, Schüller U, Vik-Mo EO, Proescholdt M, Riemenschneider MJ, Zadeh G, Ammerpohl O, Yip S, Synowitz M, van Bömmel** A, Kretzmer** H, Müller** FJ
Nat Med 2025, 31(3), 840-8 ** co-corresponding authors - The microcephaly-associated protein YIPF5 differentially regulates ER-export
Bruno F, Anitei M, Di Fraia D, Durso W, Dau T, Cirri E, Sannai M, Valkova C, Maldutyte J, A.Miller E, Rubio I, Garloff V, Kersten N, Farias G, Ori A, Mestres I, Calegari F, Kaether C
bioRxiv 2025, https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.06. - Altered translation elongation contributes to key hallmarks of aging in the killifish brain.
Di Fraia* D, Marino* A, Lee* JH, Kelmer Sacramento E, Baumgart M, Bagnoli S, Balla T, Schalk F, Kamrad S, Guan R, Caterino C, Giannuzzi C, Tomaz da Silva P, Sahu AK, Gut H, Siano G, Tiessen M, Terzibasi-Tozzini E, Fornasiero EF, Gagneur J, Englert C, Patil KR, Correia-Melo C, Nedialkova DD, Frydman** J, Cellerino** A, Ori** A
Science 2025, 389(6759), eadk3079 * equal contribution, ** co-senior authors - p53 reveals principles of chromatin remodeling and enhancer activation.
Fischer M, Schwarz* R, Riege* K, Förste S, Schwab K, Wiechens E, van Bömmel A, Hoffmann S
Nucleic Acids Res 2025, 53(11), gkaf465 * equal contribution - Subtyping Burkitt Lymphoma by DNA Methylation.
Glaser S, Wagener R, Kretzmer H, López C, Baptista MJ, Bens S, Bernhart S, Bhatia K, Borkhardt A, Elgaafary S, Hoffmann S, Hübschmann D, Hummel M, Klapper W, Kolarova J, Kreuz M, Lazzi S, Löffler M, Navarro JT, Neequaye J, Onyango N, Onyuma T, Ott G, Radlwimmer B, Rohde M, Rosenwald A, Rosolowski M, Schlesner M, Szczepanowski M, Tapia G, Wößmann W, Küppers R, Trümper L, Leoncini L, Lichter P, Del Val C, Ammerpohl O, Burkhardt B, Mbulaiteye SM, Siebert R, ICGC MMML‐Seq Consortium MMML Project
Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2025, 64(4), e70042 - Fetal-like reversion in the regenerating intestine is regulated by mesenchymal asporin.
Iqbal S, Andersson S, Nesta E, Pentinmikko N, Kumar A, Kumar Jha S, Borshagovski D, Webb A, Gebert N, Viitala EW, Ritchie A, Scharaw S, Kuuluvainen E, Larsen HL, Saarinen T, Juuti A, Ristimäki A, Jeltsch M, Ori A, Varjosalo M, Pietiläinen KH, Ollila S, Jensen KB, Oudhoff MJ, Katajisto P
Cell Stem Cell 2025, 32(4), 613-626.e8 - Lonafarnib Partially Reverses Cardiac Senescence in Human and Mouse Progeria Models via Autophagy Activation
M.Monteiro L, R.Pitrez P, Correia-Santos S, Dark N, Santinha D, Aveleira C, Townsend M, Taylor J, Nissan X, Sardão V, Cortes L, Mitter R, Marino A, Sousa-Soares C, Ribeiro R, C.Smith J, Logarinho E, Ori A, S.Bernardo A, Ferreira L
bioRxiv 2025, https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.06. - Aging and diet alter the protein ubiquitylation landscape in the mouse brain.
Marino* A, Di Fraia* D, Panfilova D, Sahu AK, Minetti A, Omrani O, Cirri E, Ori A
Nat Commun 2025, 16(1), 5266 * equal contribution - DNA damage response regulator ATR licenses PINK1-mediated mitophagy.
Marx* C, Qing* X, Gong* Y, Kirkpatrick J, Siniuk K, Beznoussenko GV, Kidiyoor GR, Kirtay M, Buder K, Koch P, Westermann M, Bruhn C, Brown EJ, Xu X, Foiani M, Wang ZQ
Nucleic Acids Res 2025, 53(5), gkaf178 * equal contribution