Subarea 5: Computational and Systems Biology of Aging
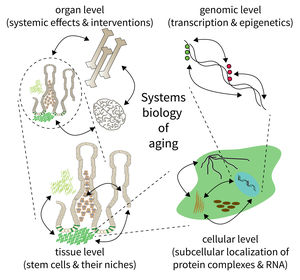
Subarea 5 focuses on the development of methods to analyse and understand complex biological systems. This work includes the design of computer algorithms and biostatistical approaches as well as the development of novel Omic strategies (i.e. genomics/epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) to study aging and aging-related diseases. According to the FLI, due to the Subarea's expertise in computational data analysis, it is deeply interconnected with all other Subareas. The Subarea hosts two critical core facilities (Life Science Computing, Proteomics) and provides consulting services in statistics. Furthermore, it organizes courses on data analysis and statistics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Mapping extrinsic and intrinsic factors influencing stem cells during aging,
- Integration of spatiotemporal proteomics and transcriptomics data,
- Comprehensive evaluation of qualitative and quantitative expression changes,
- Identification and analysis of epigenomic alterations during aging and age-related diseases, and
- Network analysis of genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic alterations during aging.
Research focus of Subarea 5.
The biology of aging can be viewed as a multilayered array of networks at the level of organs, cells, molecules, and genes. The FLI wants to meet this complexity by establishing the new Subarea on “Computational and Systems Biology of Aging”. The overall goal is to interconnect research at different scales, taking place in Subareas 1-4 of the Institute’s research program. The new group on Systems Biology will integrate data from networks at multiple scales and will thus point to mechanisms and interactions that would not be seen in unilayer approaches.
Publications
(since 2016)
2024
- The Neurolipid Atlas: a lipidomics resource for neurodegenerative diseases uncovers cholesterol as a regulator of astrocyte reactivity impaired by ApoE4
Feringa FM, Koppes-den Hertog SJ, Wang L, Derks RJE, Kruijff I, Erlebach L, Heijneman J, Miramontes R, Pömpner N, Blomberg N, Olivier-Jimenez D, Eva Johansen L, Cammack AJ, Giblin A, Toomey CE, Rose IVL, Yuan H, Ward M, Isaacs AM, Kampmann M, Kronenberg-Versteeg D, Lashley T, M.Thompson L, Ori A, Mohammed Y, Giera M, van der Kant R
bioRxiv 2024, https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07. - Gene regulation by the tumor suppressor p53 - The omics era.
Fischer M
Bba-Rev Cancer 2024, 1879(4), 189111 - Genomregulation durch Tumorsuppressoren und Onkoproteine
Fischer M
BIOspektrum 2024, 30, 123 - Determinants of p53 DNA binding, gene regulation, and cell fate decisions.
Fischer** * M, Sammons** * MA
Cell Death Differ 2024 (epub ahead of print) * equal contribution, ** co-corresponding authors - Cell-Type Resolved Protein Atlas of Brain Lysosomes Identifies SLC45A1-Associated Disease as a Lysosomal Disorder.
Ghoochani A, Heiby JC, Rawat ES, Medoh UN, Di Fraia D, Dong W, Gastou M, Nyame K, Laqtom NN, Gomez-Ospina N, Ori A, Abu-Remaileh M
bioRxiv 2024, 10.1101/2024.10.14.618295 - Systematic computational hunting for small RNAs derived from ncRNAs during dengue virus infection in endothelial HMEC-1 cells.
Gutierrez-Diaz A, Hoffmann S, Gallego-Gómez JC, Bermudez-Santana CI
Front Bioinform 2024, 4, 1293412 - Impact of inflammatory preconditioning on murine microglial proteome response induced by focal ischemic brain injury.
Helbing DL, Haas F, Cirri E, Rahnis N, Dau TTD, Kelmer Sacramento E, Oraha N, Böhm L, Lajqi T, Fehringer P, Morrison H, Bauer R
Front Immunol 2024, 15, 1227355 - Denervation alters the secretome of myofibers and thereby affects muscle stem cell lineage progression and functionality.
Henze H, Hüttner SS, Koch P, Schüler SC, Groth M, von Eyss B, von Maltzahn J
NPJ Regen Med 2024, 9(1), 10 - Bashing irreproducibility with shournal.
Kirchner T, Riege K, Hoffmann S
Sci Rep 2024, 14(1), 4872 - Pipeline Olympics: continuable benchmarking of computational workflows for DNA methylation sequencing data against an experimental gold-standard
Lin YY, Breuer K, Weichenhan D, Lafrenz P, Wilk A, Chepeleva M, Mücke O, Schönung M, Petermann F, Kensche P, Weiser L, Thommen F, Giacomelli G, Nordstroem K, Gonzales-Avalos E, Merkel A, Kretzmer H, Fischer J, Krämer S, Iskar M, Wolf S, Buchhalter I, Esteller M, Lawerenz C, Twardziok S, Zapatka M, Hovestadt V, Schlesner M, Schulz M, Hoffmann S, Gerhauser C, Walter J, Hartmann M, B.Lipka D, Assenov Y, Bock C, Plass C, Toth R, Lutsik P
bioRxiv 2024, https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.