Subarea 5: Computational and Systems Biology of Aging
Subarea 5 focuses on the development of methods to analyse and understand complex biological systems. This work includes the design of computer algorithms and biostatistical approaches as well as the development of novel Omic strategies (i.e. genomics/epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) to study aging and aging-related diseases. According to the FLI, due to the Subarea's expertise in computational data analysis, it is deeply interconnected with all other Subareas. The Subarea hosts two critical core facilities (Life Science Computing, Proteomics) and provides consulting services in statistics. Furthermore, it organizes courses on data analysis and statistics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Mapping extrinsic and intrinsic factors influencing stem cells during aging,
- Integration of spatiotemporal proteomics and transcriptomics data,
- Comprehensive evaluation of qualitative and quantitative expression changes,
- Identification and analysis of epigenomic alterations during aging and age-related diseases, and
- Network analysis of genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic alterations during aging.
Research focus of Subarea 5.
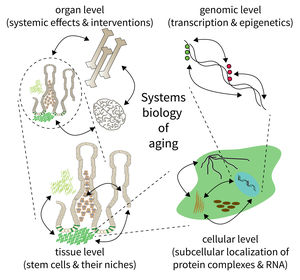
The biology of aging can be viewed as a multilayered array of networks at the level of organs, cells, molecules, and genes. The FLI wants to meet this complexity by establishing the new Subarea on “Computational and Systems Biology of Aging”. The overall goal is to interconnect research at different scales, taking place in Subareas 1-4 of the Institute’s research program. The new group on Systems Biology will integrate data from networks at multiple scales and will thus point to mechanisms and interactions that would not be seen in unilayer approaches.
Publications
(since 2016)
2023
- Short-Term Caloric Restriction and Subsequent Re-Feeding Compromise Liver Health and Associated Lipid Mediator Signaling in Aged Mice.
Schädel P, Wichmann-Costaganna M, Czapka A, Gebert N, Ori A, Werz O
Nutrients 2023, 15(16), 3660 - Multi-omics analysis identifies RFX7 targets involved in tumor suppression and neuronal processes.
Schwab K, Coronel L, Riege K, Sacramento EK, Rahnis N, Häckes D, Cirri E, Groth M, Hoffmann S, Fischer M
CELL DEATH DISCOV 2023, 9(1), 80 - Characterizing the transposome and its activity
Schwarz R
Dissertation 2023, Jena, Germany - Immunoproteasome function maintains oncogenic gene expression in KMT2A-complex driven leukemia.
Tubío-Santamaría N, Jayavelu AK, Schnoeder TM, Eifert T, Hsu CJ, Perner F, Zhang Q, Wenge DV, Hansen FM, Kirkpatrick JM, Jyotsana N, Lane SW, von Eyss B, Deshpande AJ, Kühn MWM, Schwaller J, Cammann C, Seifert U, Ebstein F, Krüger E, Hochhaus A, Heuser M, Ori A, Mann M, Armstrong SA, Heidel FH
Mol Cancer 2023, 22(1), 196 - Large-scale benchmarking of circRNA detection tools reveals large differences in sensitivity but not in precision.
Vromman M, Anckaert J, Bortoluzzi S, Buratin A, Chen CY, Chu Q, Chuang TJ, Dehghannasiri R, Dieterich C, Dong X, Flicek P, Gaffo E, Gu W, He C, Hoffmann S, Izuogu O, Jackson MS, Jakobi T, Lai EC, Nuytens J, Salzman J, Santibanez-Koref M, Stadler P, Thas O, Vanden Eynde E, Verniers K, Wen G, Westholm J, Yang L, Ye CY, Yigit N, Yuan GH, Zhang J, Zhao F, Vandesompele J, Volders PJ
Nat Methods 2023, 20(8), 1159-69 - A protocol for the use of cloud-based quantum computers for logical network analysis of biological systems.
Weidner FM, Rossini M, Ankerhold J, Kestler HA
STAR Protoc 2023, 4(3), 102438 - Leveraging quantum computing for dynamic analyses of logical networks in systems biology.
Weidner FM, Schwab JD, Wölk S, Rupprecht F, Ikonomi N, Werle SD, Hoffmann S, Kühl M, Kestler HA
PATTERNS 2023, 4(3), 100705 - Author Correction: Butler enables rapid cloud-based analysis of thousands of human genomes.
Yakneen S, Waszak SM, PCAWG Technical Working Group, Gertz M, Korbel JO, PCAWG Consortium
Nat Biotechnol 2023, 41(4), 577 - Author Correction: Comprehensive molecular characterization of mitochondrial genomes in human cancers.
Yuan Y, Ju YS, Kim Y, Li J, Wang Y, Yoon CJ, Yang Y, Martincorena I, Creighton CJ, Weinstein JN, Xu Y, Han L, Kim HL, Nakagawa H, Park K, Campbell PJ, Liang H, PCAWG Consortium
Nat Genet 2023, 55(6), 1078 - Author Correction: The landscape of viral associations in human cancers.
Zapatka M, Borozan I, Brewer DS, Iskar M, Grundhoff A, Alawi M, Desai N, Sültmann H, Moch H, PCAWG Pathogens, Cooper CS, Eils R, Ferretti V, Lichter P, PCAWG Consortium
Nat Genet 2023, 55(6), 1077