Subarea 5: Computational and Systems Biology of Aging
Subarea 5 focuses on the development of methods to analyse and understand complex biological systems. This work includes the design of computer algorithms and biostatistical approaches as well as the development of novel Omic strategies (i.e. genomics/epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) to study aging and aging-related diseases. According to the FLI, due to the Subarea's expertise in computational data analysis, it is deeply interconnected with all other Subareas. The Subarea hosts two critical core facilities (Life Science Computing, Proteomics) and provides consulting services in statistics. Furthermore, it organizes courses on data analysis and statistics.
The research is defined by five focus areas:
- Mapping extrinsic and intrinsic factors influencing stem cells during aging,
- Integration of spatiotemporal proteomics and transcriptomics data,
- Comprehensive evaluation of qualitative and quantitative expression changes,
- Identification and analysis of epigenomic alterations during aging and age-related diseases, and
- Network analysis of genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic alterations during aging.
Research focus of Subarea 5.
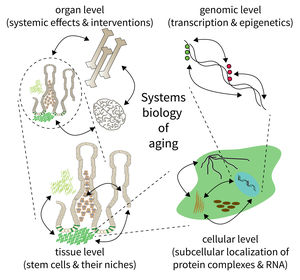
The biology of aging can be viewed as a multilayered array of networks at the level of organs, cells, molecules, and genes. The FLI wants to meet this complexity by establishing the new Subarea on “Computational and Systems Biology of Aging”. The overall goal is to interconnect research at different scales, taking place in Subareas 1-4 of the Institute’s research program. The new group on Systems Biology will integrate data from networks at multiple scales and will thus point to mechanisms and interactions that would not be seen in unilayer approaches.
Publications
(since 2016)
2024
- Mis-spliced transcripts generate de novo proteins in TDP-43-related ALS/FTD.
Seddighi S, Qi YA, Brown AL, Wilkins OG, Bereda C, Belair C, Zhang YJ, Prudencio M, Keuss MJ, Khandeshi A, Pickles S, Kargbo-Hill SE, Hawrot J, Ramos DM, Yuan H, Roberts J, Sacramento EK, Shah SI, Nalls MA, Colón-Mercado JM, Reyes JF, Ryan VH, Nelson MP, Cook CN, Li Z, Screven L, Kwan JY, Mehta PR, Zanovello M, Hallegger M, Shantaraman A, Ping L, Koike Y, Oskarsson B, Staff NP, Duong DM, Ahmed A, Secrier M, Ule J, Jacobson S, Reich DS, Rohrer JD, Malaspina A, Dickson DW, Glass JD, Ori A, Seyfried NT, Maragkakis M, Petrucelli L, Fratta P, Ward ME
Sci Transl Med 2024, 16(734), eadg7162 - Reducing the metabolic burden of rRNA synthesis promotes healthy longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Sharifi* S, Chaudhari* P, Martirosyan A, Eberhardt AO, Witt F, Gollowitzer A, Lange L, Woitzat Y, Okoli EM, Li H, Rahnis N, Kirkpatrick J, Werz O, Ori A, Koeberle A, Bierhoff** H, Ermolaeva** M
Nat Commun 2024, 15(1), 1702 * equal contribution, ** co-corresponding authors - The cytoskeletal protein Leiomodin 1 controls Sirtuin 1 localization during myogenic differentiation
Späth E
Dissertation 2024, Jena, Germany - Leiomodin 1 promotes myogenic differentiation by modulating Sirtuin 1
Späth* E, C.Schüler* S, Heinze I, Dau T, Minetti A, Hofmann M, von Maltzahn** J, Ori** A
bioRxiv 2024, https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03. * equal contribution, ** co-corresponding authors - Transthyretin orchestrates vitamin B12-induced stress resilience.
Stein G, Aly JS, Manzolillo A, Lange L, Riege K, Hussain I, Heller EA, Cubillos S, Ernst T, Hübner CA, Turecki G, Hoffmann S, Engmann O
Biol Psychiatry 2024, 97(1), 54-63 - Npbwr1 signaling mediates fast antidepressant action
Stein G, S.Aly J, Lange L, Manzolillo A, Riege K, Brancato A, A.Hübner C, Turecki G, Hoffmann S, Engmann O
bioRxiv 2024, 10.1101/2024.02.02.578166 - Proteomic profiling reveals CEACAM6 function in driving gallbladder cancer aggressiveness through integrin receptor, PRKCD and AKT/ERK signaling.
Sugiyanto RN, Metzger C, Inal A, Truckenmueller F, Gür K, Eiteneuer E, Huth T, Fraas A, Heinze I, Kirkpatrick J, Sticht C, Albrecht T, Goeppert B, Poth T, Pusch S, Mehrabi A, Schirmacher P, Ji J, Ori A, Roessler S
Cell Death Dis 2024, 15(10), 780 - An artificial intelligence-assisted clinical framework to facilitate diagnostics and translational discovery in hematologic neoplasia.
Tang M, Antić Ž, Fardzadeh P, Pietzsch S, Schröder C, Eberhardt A, van Bömmel A, Escherich G, Hofmann W, Horstmann MA, Illig T, McCrary JM, Lentes J, Metzler M, Nejdl W, Schlegelberger B, Schrappe M, Zimmermann M, Miarka-Walczyk K, Patsorczak A, Cario G, Renard BY, Stanulla M, Bergmann AK
EBioMedicine 2024, 104, 105171 - SEPTIN10-mediated crosstalk between cytoskeletal networks controls mechanotransduction and oncogenic YAP/TAZ signaling.
Weiler SME, Bissinger M, Rose F, von Bubnoff F, Lutz T, Ori A, Schirmacher P, Breuhahn K
Cancer Lett 2024, 584, 216637